What Does Lower Inflation Mean for You?
Lower inflation is a term often thrown around in economic discussions, but what does it really mean for you? As an economist from the Treasury explains, a fall in inflation means that prices are now rising more slowly. This, combined with wage growth, makes the cost of living more affordable. You can buy more with the money in your pocket, save more, and enjoy a better quality of life.
 Image: A graph showing the UK economy’s growth
Image: A graph showing the UK economy’s growth
How Will Lower Inflation Help the Economy?
Lower inflation supports people by maintaining the purchasing power of their money. If prices only rise slowly, people can plan their budgets more effectively, encouraging spending and investment, which fuels the economy. Lower inflation also helps businesses grow by providing a stable, predictable environment for them to operate in, allowing for more job opportunities or the ability to research new products and services. Finally, low inflation enhances the UK’s competitiveness in a global market. When the economy is stable and predictable, other countries are more interested in investing in the UK.
 Image: A photo of a business owner in their shop
Image: A photo of a business owner in their shop
How Will Lower Inflation Help My Business?
If inflation is lower, it means the price of materials businesses use to produce their goods and services aren’t rising as quickly, so there is less pressure on them to pass price increases onto their customers. For example, a coffee shop won’t face large increases in the cost of their coffee beans, paper cups, or the energy to turn on the lights in the coffee shop. Because none of those things are getting drastically more expensive, they don’t have to pass those costs on to coffee for their customers. Lower inflation provides a sense of stability for businesses, which is important to empower them to make decisions about their future.
 Image: A photo of a coffee shop
Image: A photo of a coffee shop
What Does Inflation Going Down Mean for My Mortgage?
Inflation influences mortgage rates indirectly, through financial market’s expectations for the Bank of England’s base interest rate. The base interest rate, which is also known as the Bank Rate, is the tool used by the Bank of England to bring inflation down. Mortgages are generally priced to reflect what the financial markets expect future interest rates to be. This means that if markets start to expect higher inflation, they will raise their expectations for the Bank Rate, in order to cool the economy and bring inflation back to target. This is in turn reflected in mortgage interest rates. If inflation falls more quickly than expected, it may lead to reductions in market expectations for the base interest rate and therefore reductions in mortgage rates offered.
Image: A graph showing mortgage rates
In conclusion, lower inflation has a positive impact on individuals and businesses alike. It provides a sense of stability, allows for better budgeting, and can even lead to lower mortgage rates. As the economy continues to evolve, it’s essential to understand the implications of inflation on our daily lives.
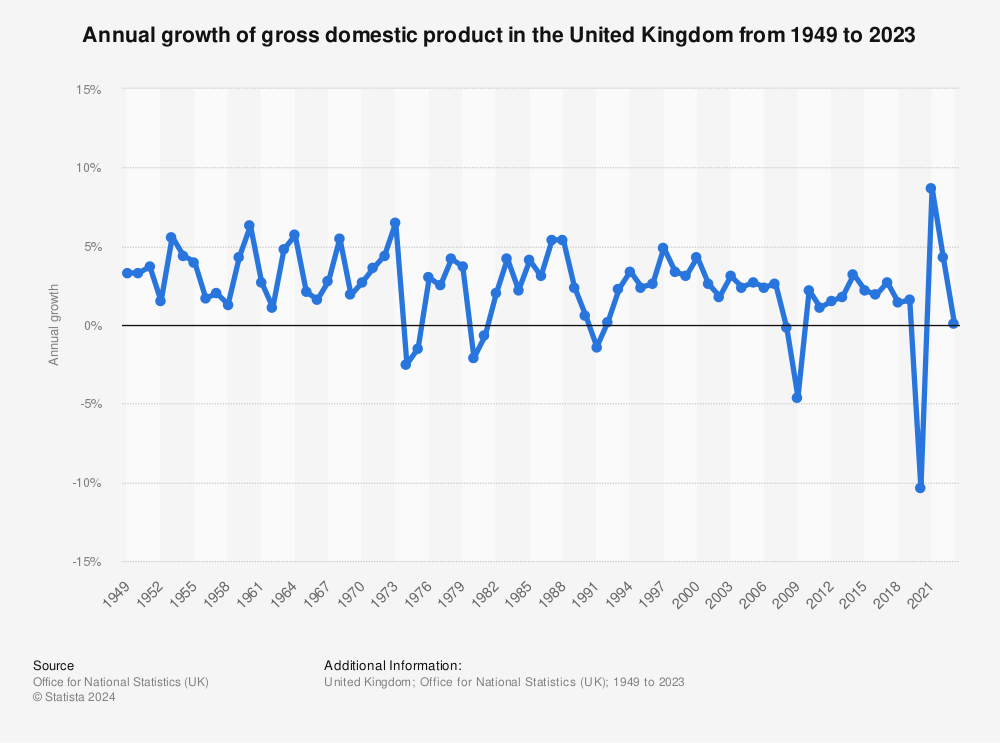 Image: A graph showing the UK economy’s growth
Image: A graph showing the UK economy’s growth